Describe the Mechanisms by Which Enzymes Lower Activation Energy
2 Enzyme may stretch the substrate molecules toward their transition site. Explain the mechanisms by which enzymes lower the activation energy of reactions.

Enzymes Ppt Video Online Download
Activation energy transition state and reaction rate.
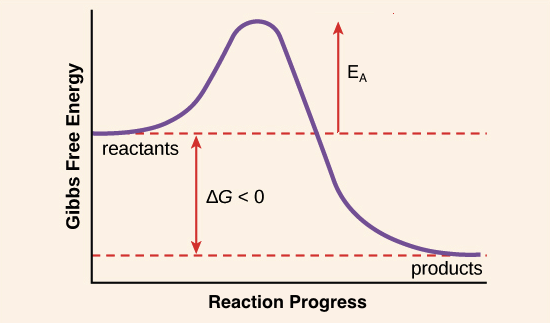
. Explain how enzymes break down macromolecules. Thats because enzymes dont affect the free energy of the reactants or products. One of the ways enzymes promote reactions is that the active sites on the enzyme molecule interact with reactants to lower the activation energy for the reaction.
Enzymes lower the activation energy they not provide activation energy. This reduces the amount of energy needed to complete the transition. Activation energy transition state and reaction rate.
Many enzymes change shape when substrates bind. The lower the activation energy for a reaction the faster the rate. Thus enzymes speed up reactions by lowering activation energy.
Binding at an active sight is. Describe four of these mechanisms. Examine Figure 615 as you develop your answer.
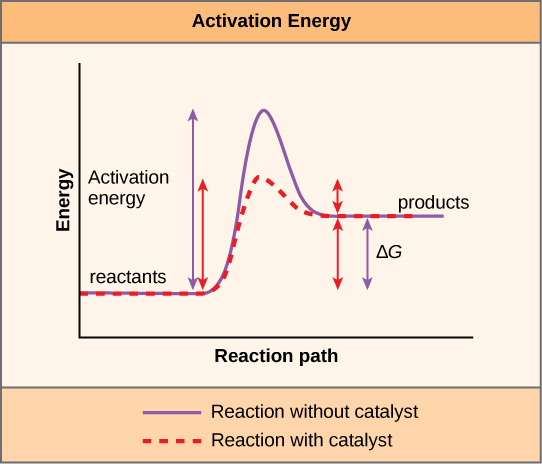
Describe what a catalyst does. Definition of an Enzyme Recall from Chapter 6 that enzymes are biological catalysts that reduce the activation energy required for a reaction to proceed in the forward direction Figure 71. Orienting substrate in positions that favor reaction.
-Describe the mechanisms by which enzymes lower activation energy and the role of the active site Question. Enzymes use a variety of mechanisms to lower activation energy. Almost all the enzymes are protein in nature except ribozymes.
What bonds are broken what bonds are formed. Helping substrates get togetherwhen substrate molecules are far apart they rarely react. Enzymes are proteins that lower the activation energy of a reaction and act as a catalyst in living organisms.
Reaction occurs activation energy lowered substrate joins the enzyme the active site products are released and enzyme available use again. Explain how cells regulate enzyme activity. The transition state is at the top of the energy hill in the diagram above.
Enzymes accelerate the rate of biochemical reaction by decreasing the energy of activation. Specific enzyme bacterial system. The enzyme-substrate complex can lower the activation energy by contorting substrate molecules in such a way as to facilitate bond-breaking helping to reach the transition state.
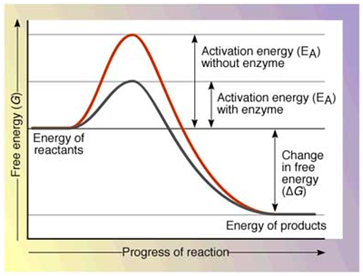
Enzymes reduce the activation energy through a process called catalysis. Enzyme structure and catalysis. As shown in Figure 3 enzymes are considered to lower the activation energy of a system by making it energetically easier for the transition state to form.
Enzymatic action can aid this process. 1 Proper orientation of the substrate 2 Stabilize transition states by straining the substrate bonds 3 providing a favorable micro environment 4 Direct participation of the active site in the chemical reaction is another mechanism of catalysis. What is the role of water.
It requires less energy for the kick start thereby accelerating the rate at which the reaction will. 1 Active site provides a template on which the substrates can come together in the proper orientation for a reaction to occur. A biochemical reaction when an enzyme is present is called a catalyzed reaction.
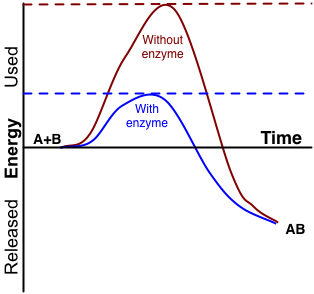
An enzyme can act in several ways to lower E_a. Rather they provide an alternative set of reactions with lower activation energies. Enzymes use a variety of mechanisms to lower activation energy.
The first of which is simply by placing substrates in contact with. Catalysis can happen in different ways. What are four mechanisms which enzymes use to lower activation energy.
Describe four of these mechanisms. This is termed induced fit meaning that the precise orientation of the enzyme required for catalytic activity. Finally enzymes can also lower activation energies by taking part in the chemical reaction itself.
How enzymes allow for lower activation energy chemical reactions self. In many cases the enzyme binds to the substrate so that the active complex. In this section we will review some fundamentals of organic and biological chemistry that are helpful in understanding enzyme reaction mechanisms.
Instead enzymes lower the energy of the transition state an unstable state that products must pass through in order to become reactants. It does this by forming an enzyme-substrate ES complex. Enzymes are able to lower activation energy and speed up reactions in four ways.
So using R for reactants C for catalyst and P for products the original reaction would be. The enzyme may create a charge distribution. There are several different mechanisms that can lead to a reduction in activation energy so that the reaction can occur.
In the presence of an enzyme catalyst the formation of the transition state is energetically more favourable ie. Learn more about the concepts of activation energy substrate enzyme-substrate. Another way enzymes can lower the activation energy by rearranging the electrons in the substrate so that there are areas that carry partial positive and partial negative charges which favor a reaction to occur.
Describe how regulation of enzyme activity helps control metabolism allosteric regulation and feedback inhibition Explain why an investment of activation energy is necessary to initiate a spontaneous reaction. Catalysts of which enzymes are a subset do not actually affect the activation energy of the original reaction of interest. The enzyme may hold the substrates in such a way as to distort the substrate bonds closer to their form in the transition state.
If youre seeing this message it means were having trouble loading external resources on our website. Describe environmental factors that affect enzyme activity. Describe a typical enzyme-substrate complex.
Enzymes are biological catalyst that catalyze biochemical reaction during metabolism but itself remain unaffected during the process of catalysis. Lastly the enzyme can strain the bound substrate which forces it to a transition state that favors a reaction. Catalysts lower the activation energy for reactions.
On their own substrates collide from random. What mechanisms do enzymes use to lower activation energy and speed up a reaction. Enzymes and the active site.
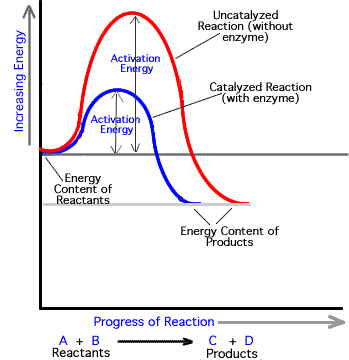
How Do Enzymes Speed Up The Chemical Reactions Use Activation Energy In Your Answer Socratic

Enzymes Biology For Non Majors I

Enzymes Effect On Activation Energy And Free Energy Youtube

Enzyme Action Measuring Rate Of Reaction Substrate Concentration The Effects Of The Following Factors On The Rate Of Enzyme Controlled Reactions Ppt Download

Enzymes Allow Activation Energies To Be Lowered Learn Science At Scitable
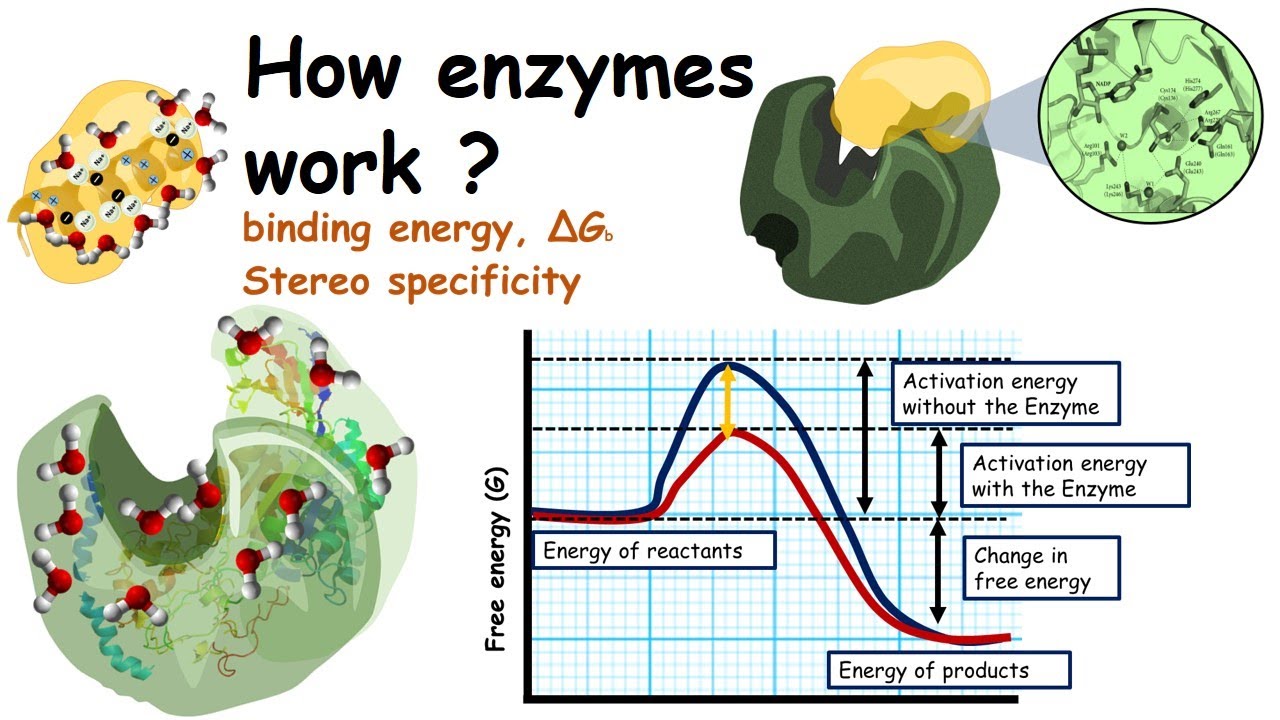
How Enzymes Work Lowering Of Activation Energy By Enzymes And Binding Energy Youtube
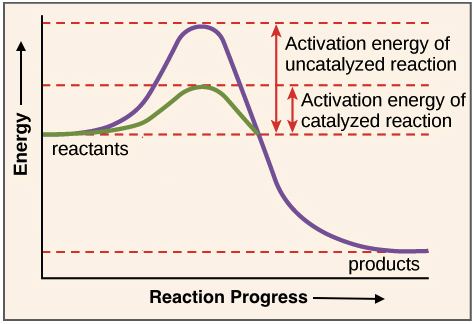
Enzymes Review Article Khan Academy

Origins Of Cell Compartmentalization Ap Biology Biology Dictionary
How To Describe The Difference Between Activation Energy And Enzymes Quora

Rate Of Reaction Enzymes Role Importance Expii
Biochemistry Activation Energy Enzymes Pathwayz

Activation Energy Article Khan Academy
How To Describe The Difference Between Activation Energy And Enzymes Quora


Comments
Post a Comment